Huawei ❤️ Rust
Our Rust Mission at Huawei
Innovations by Rust
Since 2015, Rust has consistently been voted as the most loved programming language in the StackOverflow survey.
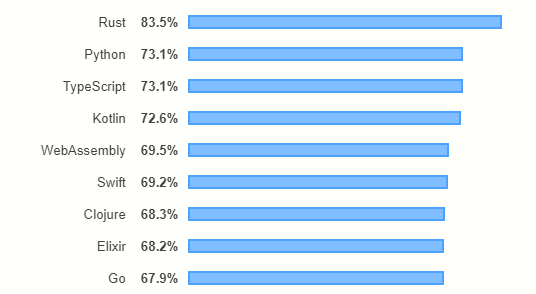
There has also been an increasing number of publications on Rust at the recent top programming languages and software engineering conferences.

If that’s not enough, a recent Nature 2020 article, `Why Scientists are Turning to Rust’, says that there is increasing momentum on the adoption of Rust amongst scientists.

Initial adoption of Rust at Huawei
At Huawei, we aim to engineer trustworthy software systems in the world’s largest telecom industry.
For example, we are working to migrate parts of our codebase towards Rust, which is safer and as performant as C/C++. To assist our developers in this process, we are leveraging the open-source C2Rust transpiler to generate Rust code directly from C. We have created automated tools to refactor and clean up this generated Rust code through source-to-source transformations.
We are also developing a rich set of internal libraries in Rust
built around an actor-based concurrency paradigm. This simplifies
asynchronous programming by leveraging Rust language features such as
async, await, etc.
All these factors have led to increased adoption of Rust withing Huawei and smooth migration from C/C++ programs, which are dominant in the telecom industry. As the leading company in this industry and a founding member of the Rust Foundation, Huawei is committed to the the success of Rust and will continue contributing back to the Rust community.
Contributions to Rust community from Huawei
We also contribute significant features back to the Rust community. For example, our recent contributions to the Rust compiler enable the compilation of Rust programs for big-endian and ILP32 variants of AArch64. These changes enable Huawei and other hardware companies to run Rust code on networking hardware which commonly uses these architecture variants. This contribution is achieved with the help of our Rust expert Amanieu d’Antras, who has pushed through these pull requests to the LLVM compiler, the libc crate, and the Rust compiler itself. These changes introduce new end-to-end cross-compilation targets for the Rust compiler, making it easier to build Rust products for bespoke hardware using a single command:
cargo build --target aarch64_be-unknown-linux-gnu
cargo build --target aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu_ilp32
cargo build --target aarch64_be-unknown-linux-gnu_ilp32
With respect to community engagement, Huawei has been leading the effort in China, strategically sponsored the first Rust China Conf during December 26-27 in Shenzhen. We have started to lead the community by carrying out several activities, including creating Rust tutorials and Rust coding conventions in Chinese for a vast number of developers who are interested in Rust.
Adapting end-to-end Rust tooling for Huawei
There are many end-to-end tools out there in the Rust community and we have started to benefit from the interactions with developers of these tools.
Here are just a few examples.
tokei
Because trustworthy programming typically involves migrating programming
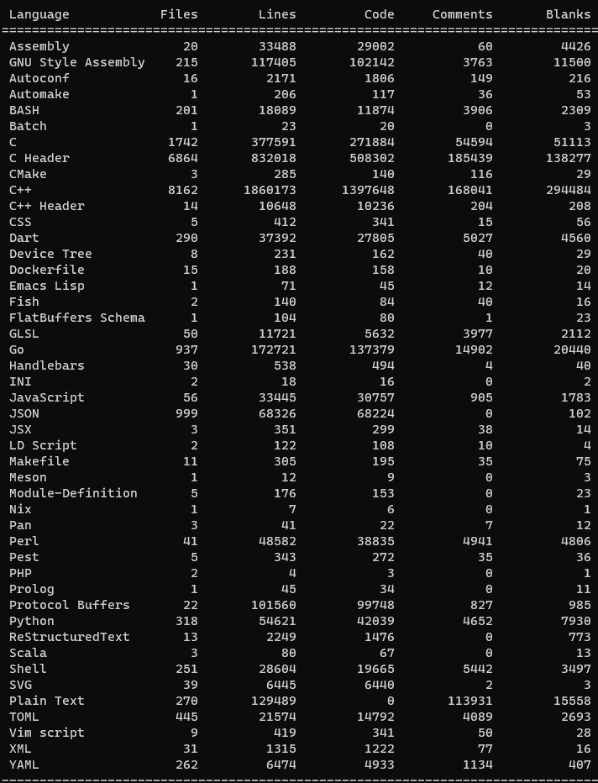
languages, we have adopted tokei as our code
complexity metrics tool, which can recognize as many as 200 languages. For
For example, the following statistics show how many lines of code various
programming languages have been developed in Google’s Fucshia project:
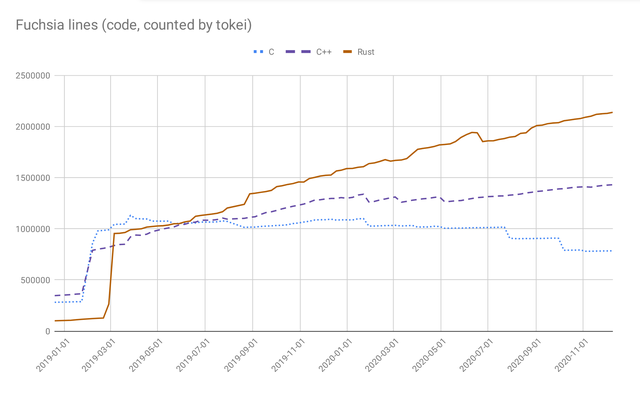
It is relatively easy to plot the proportion of C, C++, Rust code in the evolution of Fucshia, as follows:
To accommodate the needs to processing multiple programming languages
in our projects, we have made a pull request to
tokei to support batch
processing of recognized languages.
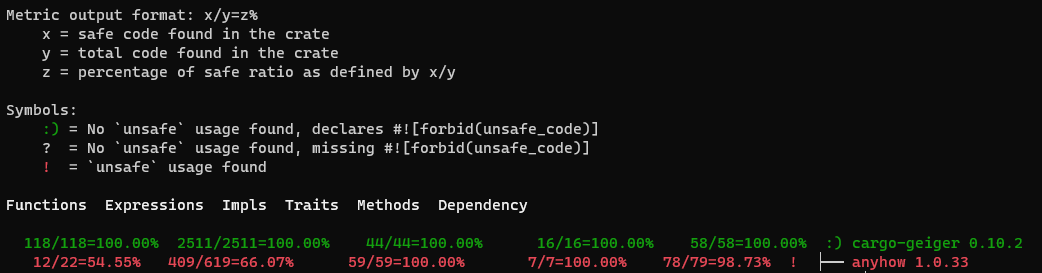
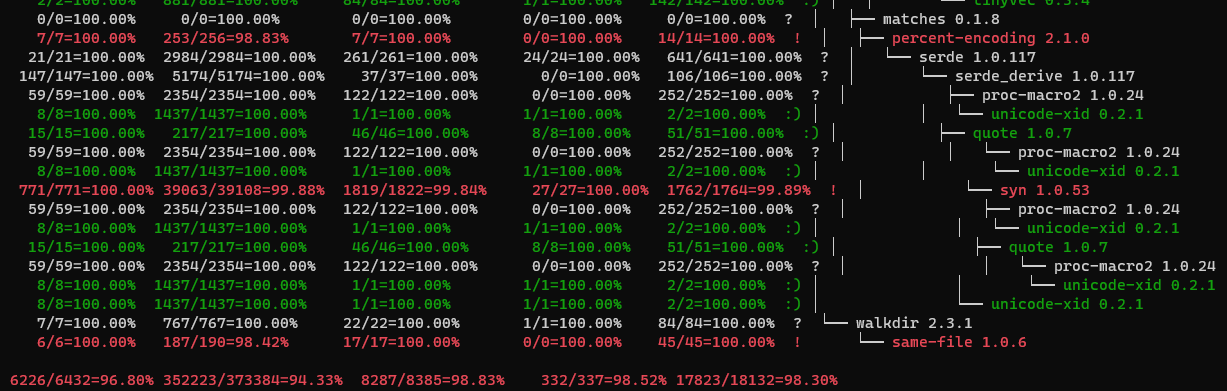
cargo-geiger
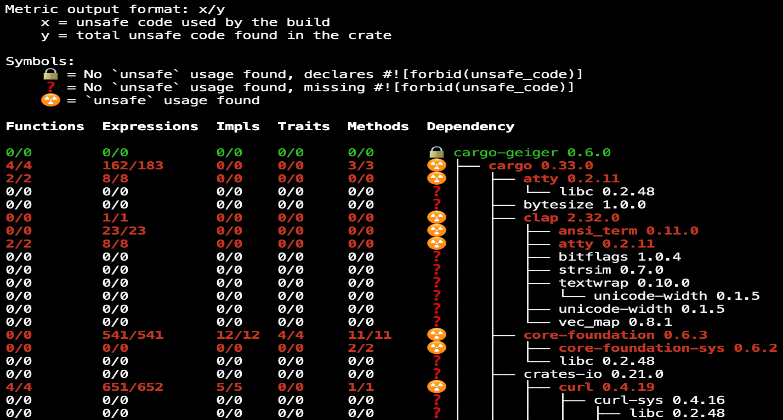
To improve safety, we would like to know how much code has been checked by the Rust
compiler. Fortunately,
cargo-geiger does almost
this by counting the statistics of unsafe items such as fn, expr,
struct, impl, trait, and their occurrences in various dependent crates:
However, the statistics do not reflect the ratio of safe items, hence not
showing how much has been achieved overall for Rust projects. Therefore, we
made a pull request to
cargo-geiger to report the checked safe ratios of Rust projects. After it was
accepted, this tool has been used regularly by our product teams on daily
basis. A report will look like the following, which has made it easier to tell
which crates have not been fully checked by the Rust compiler:
Research on Rust through Deep Code Learning
As codebases from the Rust open-source community evolve and grow, new developers need to learn the best practices, including but not limited to the language itself. Statistical machine learning methods from a large amount of source code, also known as Big Code, have been considered by software engineering research communities: similar to the machine-learning problems for image processing and natural language processing where a vast number of features requires deep neural networks (DNN) to extract, big code may also be used to train a DNN to reflect on statistical patterns of programs, which is called `Deep Code Learning’.
In this respect, Huawei is pushing the limits by improving the state-of-the-art of `cross-language’ deep code learning, through a technical collaboration with The Open University, UK and Singapore Management University.
For example, initial deep code learning methods are trained and evaluated using the benchmarks of 52,000 C/C++ programs of 104 algorithm classes collected from the programming courses of Peking University. Traditionally, tree-based convolution neural networks (TBCNN) could achieve 94% accuracy in algorithm classification for this dataset (AAAI’16). A recent progress of the SOTA using abstract syntax trees at the statement level (ICSE’19) achieved 98% accuracy. Our recent progress pushes the SOTA even higher to achieve 98.4% accuracy (AAAI’21) by an innovation on Tree-based Capsule Networks.
Earlier, we have used cross-language datasets to show that the learned model of one language applies to another programming language. For example, using the Rosetta Code datasets from Github, we show it possible to obtain 86% accuracy for algorithm classification (Java to C) (SANER’19), and cross-language API mapping problems (Java to C#) (ESEC/FSE’19). These statistical language models have found multiple applications to software engineering, in terms of code classification, code search, code recommendation, code summary, method name prediction, and code clone detection (ICSE’21). Such models also have the capability to transfer the knowledge across many tasks, thus it will reduce the effort to retrain the models for each of the tasks separately.
To analyze Rust projects, we have made another pull request to the Rust parser
project tree-sitter
and XML serialization crate
quick-xml, which allow us to
feed the abstract syntax trees of Rust programs to train a deep code learning
model. The preliminary results are quite promising, the detection algorithms in
Rust can reach an accuracy as high as 85.5\%. This number is still climbing
as we continue working on improving toolchains.
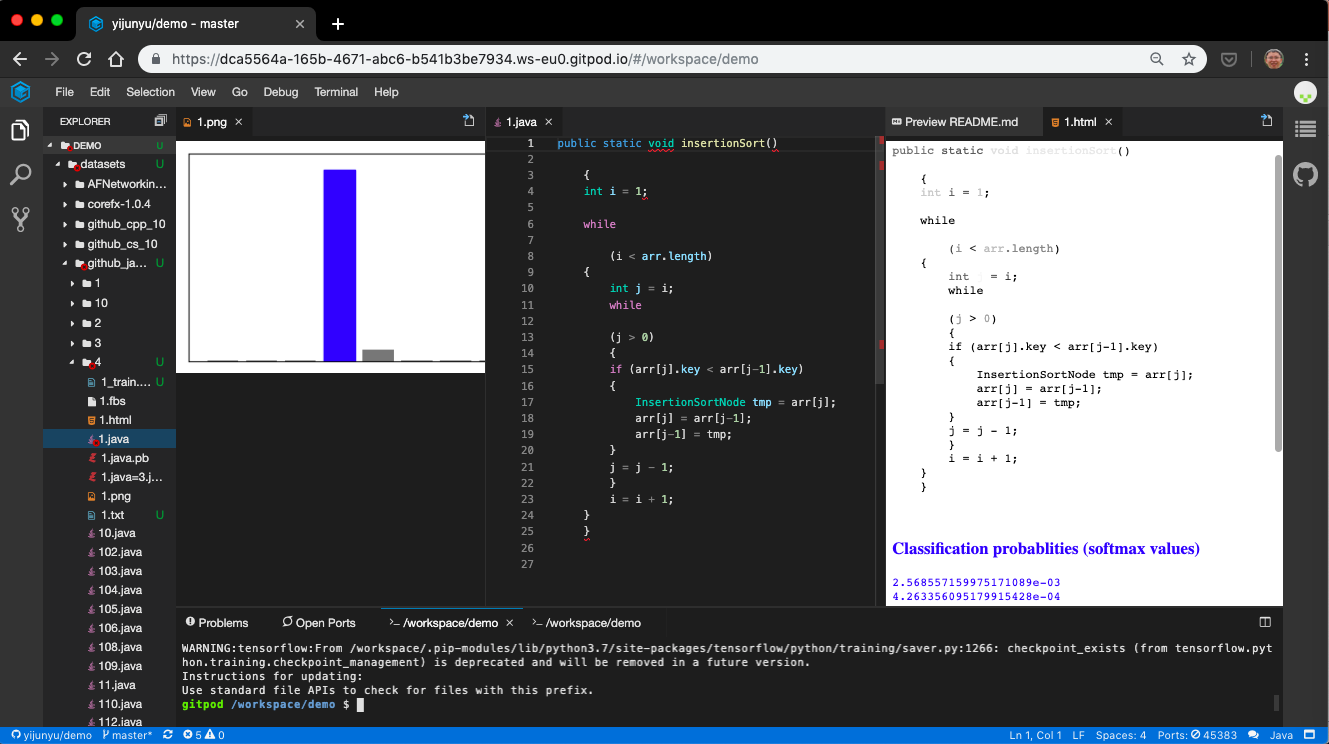
A prototype of such an IDE is shown as an extension to the Visual Studio Code,where programmers are assisted with the recommendation of a suitable algorithm and an explanation of the choice.
Conclusion
In summary, the Huawei Trustworthy Open-Source Software Engineering Lab is working hard to provide programmers an end-to-end IDE toolchain that intelligently assists in maximizing safety and performance.
A journey towards the vision of Trusted Programming has just begun and we hope to work collaboratively with the Rust community, and the upcoming Rust Foundation, to lead a smooth revolution to the Telecom software industry.
Rust带来的创新
StackOverflow的调查表明, 自2015年以来,Rust一直是开发者最爱的编程语言。

学术界对于Rust也越来越重视,在编程语言和软件工程顶会上发表的关于Rust的论文正逐年增加。

不仅如此,《自然》杂志2020年尾的文章《Why Scientists are Turning to Rust》中也强调:科学家极为推崇Rust。

Rust在华为的初步推进
华为的目标是引领通信系统软件向安全可信演进,其中Rust语言正在发挥很大的作用。
例如,我们希望通过部分C/C++代码的迁移,在保证高性能的同时,拥有更高的安全性。在此过程中, 我们为开发者提供一套自动化工具支持:基于开源的C2Rust转译工具, 首先从C代码生成Rust代码, 然后通过源到源变换工具自动重构。
在华为内部我们还基于actor的并发编程模式开发了Rust库,方便程序员充分利用
Rust的语言特性, 例如async, await等。
以华为代表的通信系统软件的开发以C/C++代码为主, 这些Rust库将使C/C++到Rust的迁移更加顺畅。 作为业界领先公司和Rust基金会的创始成员,华为致力于Rust在通信软件行业,并将持续为Rust社区做出贡献。
华为对Rust社区的贡献
我们为Rust社区贡献了许多重要的功能特性。例如,我们最近为Rust编译器提交了一系列代码,使得Rust编译目标可以支持ARM AArch64 32位大端变体ILP32芯片组, 用于我们的通信产品中。 这些改进使得我们和友商可以在这些常用网络硬件架构上执行Rust原生程序。这些代码已经通过我们的Rust专家Amanieu d’Antras 提交给了LLVM 编译器, libc库, 以及Rust编译器等开源社区。
这些对Rust编译器的更改引入了新的端到端交叉编译目标,针对定制硬件构建Rust产品变得更容易,只需要简单的命令,比如:
cargo build --target aarch64_be-unknown-linux-gnu
cargo build --target aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu_ilp32
cargo build --target aarch64_be-unknown-linux-gnu_ilp32
华为在中国Rust社区方面也走在前列,战略支持12月26日至27日在深圳举办了第一届Rust China Conf大会,并推行多项 社区活动,包括为中国的开发者提供Rust教程和Rust编码规范。
配置华为的端到端Rust工具链
Rust社区中有几种端到端的工具,我们已经开始从开发人员和工具的交互中获取信息。
这里有一些例子
tokei
由于可信编程项目通常涉及多个编程语言,我们采用了tokei作为多语言代码复杂性度量工具,识别多达200种编程语言。例如,开源的Fuchhia项目涉及了多种编程语言,下面的统计信息显示有多少行不同语种的代码:

C、C++、Rust代码在Fuchhia项目的占比,可以绘制成如下演进图:

为了在大型项目中满足处理多种编程语言的场景需求,我们提交代码到tokei支持识别编程语言的批处理。
cargo-geiger
为了提高安全性,我们经常想知道有多少代码已经被Rust编译器检查过。幸运的是,通过统计”不安全”项目,如fn、expr,struct、impl、trait及其在各相关库实现中的出现次数,
cargo-geiger几乎做到了这点。

不过,统计数字中并没有反映安全性,所以没办法展现Rust项目总体上取得了多少进展的比例。因此,我们
提交了代码,在改进的cargo-geiger计数器报告中提供Rust项目的安全检查比率。这个代码采纳后,我们的产品团队现在每天定期都在使用这个工具,一份典型的报告能够更容易理解哪些代码库还没被Rust编译器完全检查到。


通过深度代码学习研究Rust
随着Rust开源社区代码的发展和革新,初学者需要学习掌握Rust最佳的实践,其包括但不限于Rust语言本身。把统计机器学习的方法应用到源代码数据上,也称为大代码,正被全世界的软件工程研究团队关注:类似于 图像处理和自然语言处理中的机器学习问题,这些问题都需要通过深度神经网络(deep neural networks DNN)提取大量的特征,Big Code可能同样需要去训练DNN来反映程序的统计特性,所以也称为”深度代码学习”。
在这方面,华为与英国开放大学和新加坡管理大学进行技术合作,在现在最先进的“跨语言”深度代码学习基础上进行优化研究。
例如,最初的深度代码学习方法应用于北京大学编程课程收集到的104个算法类的5.2万个C/C++程序。对此数据集,树基卷积神经网络(TBCNN)算法分类准确率达到94%(AAAI’16)。最近的SOTA在语句级使用抽象语法树 (ICSE ‘19)准确率达到98%。近期我们同英国开放大学和新加坡管理大学在树基胶囊网络的合作研究进展推动了SOTA进一步提高,达到98.4%的准确率(AAAI’21)。
早些时候我们已经使用跨语言的数据集表明,对一种编程语言的深度代码学习模型也适用于另一种编程语言。例如,从GitHub爬取的数据集Rosetta Code,从Java到C语言,可以获得86%的算法分类准确度 (SANER’19),在Java到C#的跨语言API映射 问题也能发挥重要作用(ESEC/FSE’19)。这些统计语言模型在软件工程中可以应用于很多方面,比如代码分类、代码搜索、代码推荐、代码摘要、方法名称预测、代码克隆检测等等(ICSE’21)。
为了进一步研究分析Rust项目,我们向Rust解析器项目tree-sitter和XML序列化 quick-xml等项目提交了代码,通过 Rust程序的抽象语法树来训练深度代码学习模型。研究的初步结果很有希望,算法检测任务在 Rust代码上的精度高达85.5%。随着工具链的改进,这个比例还有望进一步提升。
在IDE上的原型是在Visual Studio Code IDE上,我们开发扩展插件,使得程序员可以得到合适的算法推荐和可解释性的帮助。

结论
综上所述,华为可信开源软件工程实验室正在开展的Rust工作为程序员提供智能化端到端IDE工具链,以期最大限度地提高代码的安全性和性能。走向可信编程远景的旅程刚刚开始,我们希望与Rust社区和即将成立的Rust基金会深度合作,引领电信软件产业的可信革新。
© Trusted Programming Team, Huawei


